Understanding the Different Types of Wire Cutters
Wire cutters are an essential tool for DIY enthusiasts, handymen, and professionals alike. This article provides an in-depth look at the various types of wire cutters available, their applications, and how to choose the right one for your needs.
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Wire Cutters
- Types of Wire Cutters
- Diagonal Cutters
- Flush Cutters
- End Cutters
- Shear Cutters
- Cable Cutters
- Bolt Cutters
- Choosing the Right Wire Cutter
- Proper Use and Maintenance of Wire Cutters
- Difference Between Wire Cutters and Wire Strippers
- How to Identify the Correct Cutter for Different Wire Gauges
- Common Mistakes When Using Wire Cutters and How to Avoid Them
- Conclusion
Introduction to Wire Cutters
Wire cutters are versatile tools used for cutting through various materials such as wires, cables, and even small metal objects like bolts and nails. They come in different shapes and sizes, each designed for specific cutting tasks.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide on the different types of wire cutters and their applications to help you make an informed decision when purchasing one for your toolbox.
Types of Wire Cutters
Diagonal Cutters
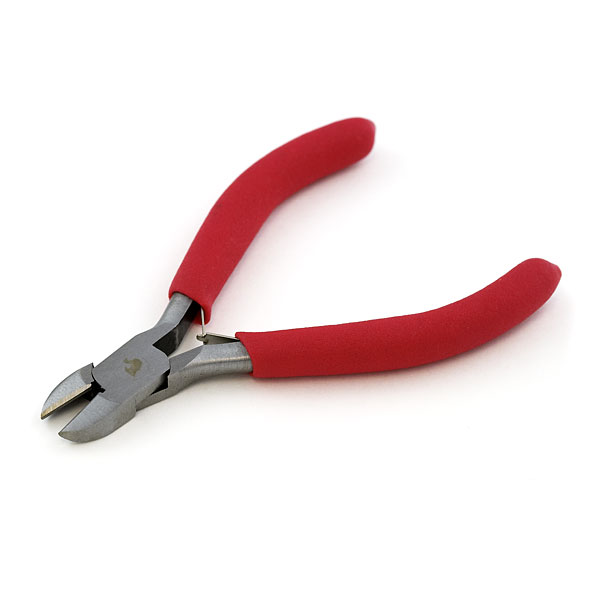

Diagonal cutters, also known as side cutters or dikes, are one of the most common types of wire cutters. They feature a sharp, angled cutting edge that allows for precise cuts in tight spaces. Diagonal cutters are ideal for cutting small wires, such as those found in electronics, and can also be used for trimming excess material from components or cutting through zip ties.
- Standard Diagonal Cutters: The most common type of diagonal cutter, featuring a standard cutting edge and general-purpose design. These are suitable for cutting various materials, including copper and aluminum wires.
- High Leverage Diagonal Cutters: These cutters have longer handles, providing increased leverage for cutting through thicker or harder materials with less effort. They are ideal for heavy-duty applications and can handle materials such as steel wires and nails.
- Insulated Diagonal Cutters: Designed for electrical work, these cutters feature insulated handles to protect against electric shock when working with live wires. They are perfect for electricians and DIYers working on home wiring projects.
Flush Cutters

Flush cutters, also known as micro cutters or nippers, are designed to make clean, flush cuts on small wires and components. They feature a flat cutting edge that allows the user to trim wires and other materials without leaving a sharp or jagged edge. Flush cutters are commonly used in electronics, jewelry making, and other precision tasks.
- Tapered Head Flush Cutters: These cutters have a tapered head that allows for greater access in tight spaces. They are perfect for cutting small wires and components in densely packed electronic devices.
- Angled Head Flush Cutters: Featuring an angled head, these cutters provide better visibility and control when cutting small wires and components. They are commonly used in jewelry making and other fine-detail work.
End Cutters

End cutters, also known as nippers or pincers, are designed for cutting through materials at a perpendicular angle. They feature a broad, flat cutting surface that makes it easy to cut materials flush against a surface. End cutters are commonly used for cutting nails, screws, and other fasteners, as well as trimming excess material from components.
- Standard End Cutters: These cutters have a general-purpose design, suitable for cutting various materials. They are ideal for cutting nails and screws flush against a surface.
- High Leverage End Cutters: With longer handles, these cutters provide increased leverage for cutting through thicker or harder materials. They are perfect for heavy-duty applications such as cutting through steel nails or bolts.
Shear Cutters

Shear cutters, also known as shears or scissors, feature a scissor-like design with two cutting edges that slide past each other when the handles are squeezed. This design allows for clean, precise cuts with minimal distortion of the material being cut. Shear cutters are ideal for cutting through cables, wires, and other materials that require a clean, smooth edge.
- Cable Shear Cutters: These cutters are specifically designed for cutting through cables, such as coaxial and Ethernet cables. They provide clean, precise cuts without damaging the internal conductors.
- Wire Shear Cutters: Designed for cutting through wires, these cutters provide a clean, smooth cut that minimizes damage to the wire's insulation. They are commonly used in electrical work and electronics.
Cable Cutters
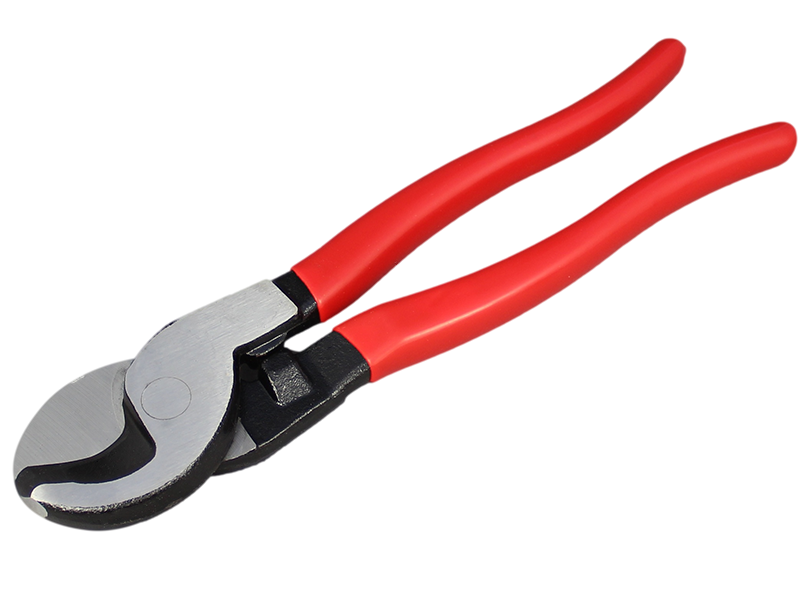

Cable cutters are designed for cutting through thick cables and wires, such as those used in electrical installations and telecommunications. They feature large, curved cutting blades that can easily cut through thick cables without crushing or distorting the internal conductors. Cable cutters come in various sizes, with larger models capable of cutting through cables up to several inches in diameter.
- Ratcheting Cable Cutters: These cutters feature a ratcheting mechanism that provides increased cutting force, making it easier to cut through thick cables. They are ideal for heavy-duty applications and cutting large-diameter cables.
- Compact Cable Cutters: Designed for smaller cables, these cutters provide a clean, precise cut without taking up too much space in your toolbox. They are perfect for DIY enthusiasts and professionals working on smaller-scale projects.
Bolt Cutters

Bolt cutters are heavy-duty tools designed for cutting through large bolts, chains, and other hard materials. They feature long handles and strong, hardened steel jaws that provide the necessary leverage and cutting force to cut through thick metal objects. Bolt cutters come in various sizes, with larger models capable of cutting through bolts and chains up to several inches in diameter.
- Standard Bolt Cutters: These cutters have a general-purpose design suitable for cutting through various materials, including bolts, chains, and padlocks.
-
Compact Bolt Cutters: Designed for smaller cutting tasks, these cutters provide the same cutting force as their larger counterparts but in a more compact form factor. They are perfect for cutting through smaller bolts and chains.
Choosing the Right Wire Cutter
When selecting a wire cutter, consider the following factors:
- Material: Choose a wire cutter designed to handle the specific material you will be cutting, such as copper, aluminum, or steel.
- Size: Select a wire cutter that can accommodate the size of the wires or cables you will be working with.
- Application: Consider the specific tasks you will be performing, such as cutting through thick cables, trimming small components, or working on electrical wiring.
- Ergonomics: Look for wire cutters with comfortable, non-slip handles that provide a secure grip during use. Insulated handles are essential when working with live wires.
Proper Use and Maintenance of Wire Cutters
To ensure the longevity and performance of your wire cutters, follow these guidelines:
- Use the correct tool for the job: Do not use a wire cutter designed for small wires to cut through thick cables or bolts. Doing so may damage the tool and result in an unsafe cutting situation.
- Keep the cutting edges sharp: Dull cutting edges can lead to poor cutting performance and increased wear on the tool. Sharpen or replace the cutting edges as needed.
- Clean and lubricate regularly: Keep your wire cutters clean and well-lubricated to prevent rust and ensure smooth operation.
- Store properly: Store your wire cutters in a dry, protected area when not in use to prevent damage and corrosion.
Difference Between Wire Cutters and Wire Strippers
When navigating the intricate world of electrical work and DIY projects, it becomes essential to understand the fundamental tools that facilitate these tasks, specifically wire cutters and wire strippers. Both tools are crucial for anyone working with electrical wiring, yet they serve distinctly different purposes. Wire cutters are primarily designed for cutting through various types of wire, making clean cuts that can range from fine, delicate wires to heavier gauge cables, while wire strippers are engineered to remove the insulating coating from wires, exposing the conductive metal beneath without damaging it. This differentiation is not only vital for effective work but also crucial for ensuring safety and preventing damage to components.
The choice between wire cutters and wire strippers hinges on the specific task at hand. Utilizing the wrong tool can lead to inefficient work, increased effort, and potential safety hazards. For instance, attempting to strip wire insulation with a cutter could damage the wire itself, resulting in poor electrical connections or even shorts. Conversely, using strippers for cutting might not yield a clean cut, leading to frayed ends that complicate connections. Recognizing these distinctions allows professionals and DIY enthusiasts alike to select the right tool for their needs, streamlining their processes and enhancing overall productivity.
Understanding Wire Cutters
Wire cutters, often referred to as wire snips or diagonal cutters, are designed with sharp, angled blades that allow for precise cutting. These tools come in various forms, each suited to different types of tasks, making it essential to choose the right style for your specific needs.
- Types of Wire Cutters:
- Diagonal Cutters: These are ideal for cutting soft, thin wires and are characterized by their angled blades, which allow for easy access in tight spaces.
- Flush Cutters: Designed to make flush cuts against surfaces, these cutters are perfect for trimming wire ends neatly and are commonly used in jewelry making and electronics.
- Heavy-Duty Cutters: For thicker or more robust wires, heavy-duty cutters are required. They typically feature longer handles to provide increased leverage, making it easier to cut through harder materials.
Understanding Wire Strippers
Wire strippers are specialized tools designed to remove insulation from wire without damaging the conductive metal underneath. They come equipped with multiple notches or blades, each corresponding to different wire gauges, enabling users to strip insulation effectively.
- Types of Wire Strippers:
- Manual Wire Strippers: These tools require the user to manually position the wire and squeeze the handles to remove insulation. They offer precision but demand a certain level of skill.
- Automatic Wire Strippers: These more advanced tools automatically grip and strip wire when the user pulls the trigger or squeezes the handles. This automation simplifies the process, especially for those who work with various wire sizes frequently.
Key Differences
Understanding the core distinctions between wire cutters and wire strippers is essential for effective use:
- Functionality: Wire cutters focus on cutting, while strippers concentrate on insulation removal.
- Design: Cutters typically have sharp, angled blades for cutting through wire, whereas strippers feature notches for accommodating various wire sizes.
- Usage Context: Cutters are used for tasks such as trimming wires or cutting cables, while strippers are essential for preparing wires for connections.
Selecting the appropriate tool not only enhances efficiency but also ensures the integrity of your work. Using a wire cutter when you need to strip wire can lead to damaged wires, while using a stripper to cut can produce jagged edges, complicating subsequent connections.
Understanding the differences between wire cutters and wire strippers is essential for anyone involved in electrical work or DIY projects. Each tool is tailored for a specific function, and recognizing their unique capabilities will lead to more effective and safer work practices.
How to Identify the Correct Cutter for Different Wire Gauges
Choosing the right wire cutter for various wire gauges is fundamental for achieving optimal results in any electrical project. Different wire gauges have specific characteristics, such as thickness and material composition, which dictate the type of cutter best suited for the task. Understanding these factors not only enhances efficiency but also ensures safety and quality in electrical work.
When selecting wire cutters, the wire gauge is one of the most critical considerations. Wire gauges are measured according to the American Wire Gauge (AWG) system, where a lower number indicates a thicker wire. This means that a 10 AWG wire is thicker than a 20 AWG wire. The specific requirements of each gauge dictate the type of wire cutter to use, and employing the wrong tool can lead to inefficiencies or damage to the wire.
Understanding Wire Gauge
Wire gauge refers to the diameter of the wire, which affects its electrical capacity and the type of cutter needed. Each gauge has distinct characteristics that influence how it should be handled.
- Thicker Wires (Lower AWG): Thicker wires, such as 10 or 12 AWG, are typically made from heavier gauge copper or aluminum. Cutting these wires requires heavy-duty cutters designed to handle increased resistance and leverage.
- Thinner Wires (Higher AWG): Thinner wires, such as 20 or 22 AWG, are often used in more delicate applications, such as electronics or small appliances. These can usually be cut with standard wire cutters, but care must be taken to ensure clean cuts to prevent fraying.
Choosing the Right Cutter
Selecting the appropriate cutter based on wire gauge involves understanding the types of wire and their associated requirements. Here are some steps to consider:
- Identify the Wire Gauge: Determine the AWG of the wire you are working with. This information is often printed on the insulation.
- Choose the Correct Tool: Select a cutter that matches the wire gauge. For example:
- 10-12 AWG: Use heavy-duty wire cutters or ratcheting cutters for added leverage.
- 14-16 AWG: Standard wire cutters should suffice, but ensure they are rated for the specific wire type.
- 18-20 AWG: Utilize precision snips or flush cutters for delicate tasks to ensure clean cuts.
- Test Cuts: Before undertaking significant cutting tasks, test your chosen cutter on a scrap piece of wire to ensure it provides the necessary leverage and cut quality.
Practical Considerations
When working with different wire gauges, several practical considerations must be taken into account:
- Material Composition: Copper wire, for instance, is softer and easier to cut compared to aluminum wire, which may require different tools.
- Insulation Thickness: Some wires have thicker insulation, requiring tools that can slice through both the wire and insulation cleanly.
- Frequency of Use: If you frequently work with a variety of wire gauges, consider investing in a versatile wire cutter that accommodates multiple sizes efficiently.
Selecting the correct wire cutter based on wire gauge is a crucial aspect of ensuring successful electrical work. By understanding the characteristics of wire gauges and choosing the right tool for the job, you can significantly enhance both efficiency and safety in your DIY projects.
Common Mistakes When Using Wire Cutters and How to Avoid Them
Engaging in electrical work, whether for professional purposes or DIY projects, often involves the use of wire cutters. However, many individuals make common mistakes that can lead to inefficiencies, unsafe practices, and damaged components. Understanding these pitfalls is crucial for anyone looking to enhance their proficiency with wire-cutting tools and achieve quality results in their projects.
Improper use of wire cutters not only affects the quality of the work but also poses safety risks. Cutting the wrong type of wire, applying excessive force, or using dull tools can result in a myriad of issues. For example, cutting through harder materials than intended can damage the blades, while attempting to cut wires without adequate support can lead to accidents. Recognizing these mistakes and implementing corrective measures can significantly improve both the process and outcome of electrical work.
Mistake #1: Using the Wrong Tool for the Job
One of the most prevalent mistakes is selecting the incorrect type of cutter for the task. Each type of wire cutter is designed for specific functions, and using the wrong tool can lead to poor results.
- Examples:
- Using Diagonal Cutters on Heavy-Duty Wire: Attempting to cut thick wires with diagonal cutters may result in damaging the tool and producing frayed wire ends.
- Using Wire Strippers as Cutters: While strippers can cut, they are not designed for this purpose and can lead to damaged wires or insulation.
Mistake #2: Neglecting Wire Gauge Considerations
Failing to consider the wire gauge when cutting is another common error. Each gauge requires specific handling and cutting techniques, and overlooking this can lead to subpar work.
- Consequences:
- Thinner Wires: Attempting to cut thinner wires with heavy-duty cutters can result in crushing the wire or causing it to fray.
- Thicker Wires: Using precision cutters on thicker wires can lead to ineffective cuts and increased effort.
Mistake #3: Inadequate Tool Maintenance
Regular maintenance of wire cutters is essential for optimal performance. Neglecting this aspect can lead to tools becoming dull, which compromises their effectiveness.
- Best Practices:
- Regular Cleaning: After each use, wipe the blades with a clean cloth to remove any debris or residue.
- Sharpening Blades: Periodically check the sharpness of the blades and sharpen them as needed to ensure clean cuts.
- Storage: Store cutters in a dry environment and avoid placing them in direct contact with other tools to prevent blade damage.
Strategies to Avoid Mistakes
To prevent the common mistakes associated with wire cutters, consider the following strategies:
- Education: Familiarize yourself with the various types of wire cutters and their intended uses. Invest time in reading manuals or guides that explain the specifics of each tool.
- Practice: Before starting significant projects, practice on scrap wire to develop a feel for the tools and techniques required for effective cutting.
- Ask for Help: If you're uncertain about the correct tool or technique, don’t hesitate to seek guidance from more experienced individuals or professionals.
By being aware of these common mistakes and implementing strategies to avoid them, you can enhance your proficiency with wire cutters. This knowledge not only improves the quality of your work but also ensures a safer and more efficient electrical project experience.
Conclusion
Wire cutters are an essential tool for anyone who works with wires, cables, and other materials that require precise cutting. With various types of wire cutters available, it is crucial to choose the right one for your specific needs and applications.
By understanding the different types of wire cutters and their uses, you can make an informed decision and ensure that you have the proper tool in your toolbox.
Proper use and maintenance of your wire cutters will ensure that they provide years of reliable service, making your DIY projects, home repairs, and professional tasks easier and more efficient.



